R-Leaf® is an innovative technology developed by Crop Intellect Ltd converting air pollution into fertiliser. Specifically, R-Leaf captures atmospheric nitrogen oxides (NOx) and through photocatalysis using day light converts them into nitrogen fertiliser
The technology is embedded into a liquid fertiliser formulation and sprayed tank-mixed on plant surfaces using standard farm sprayers.
What does it do?
The photocatalyst in R-Leaf is a specially processed titanium dioxide with enhanced ability to produce nitrogen daily whilst remaining on plant leaves for several weeks. This makes it a valuable tool for farmers to reduce their reliance on synthetic nitrogen fertilisers resulting in increased soil resilience and reduced carbon footprint without yield compromise.

How does it do it?
R-Leaf® captures soil derived NOx and from the air and converts it to nitrate. This process occurs daily on the surface of sprayed plants resulting in a supply of nitrogen to the crop daily. This can allow a reduction in the application of bulk nitrogen used.
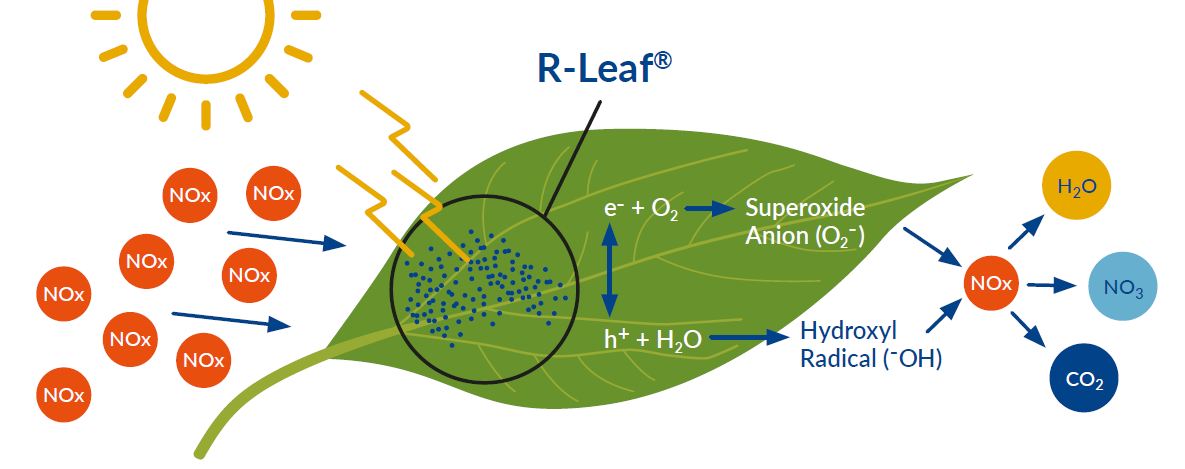
Features
Reduced air pollution
Chemical stability
Safe for crops
Can be tank mixed with most agrochemical inputs
Benefits
Environmental benefits
Reduced pollution
Cost effective
Increased crop yield
Application
R-Leaf® is sprayed onto any crop. It is a stable suspension concentrate and can be tank mixed with most agrochemical inputs. It contains 500g of the specially processed photocatalytic material. It is classed as EC fertiliser containing zinc, molybdenum and manganese which are very often deficient, particularly in cereals, and are essential elements for yield security.
The recommended dosage of R-Leaf® is 1 l/ha. The best application timing for cereals is at T1 and T2 when the soil-applied nitrogen is starting to produce NOx and when the foliage is adequate to hold R-Leaf®. The T2 application is essential as the sprayed leaves are shaded by the new ones and therefore become less efficient.
Results
The photocatalytic activity of R-Leaf® under UV and normal light was tested by independent experts in photocatalysis at Manchester Metropolitan University. The approved method measuring photocatalysis was by monitoring the CO2 in a specific reaction and results are shown below. The material was 10 times more effective in photocatalysis, both under UV light and normal light, compared to the unprocessed material.
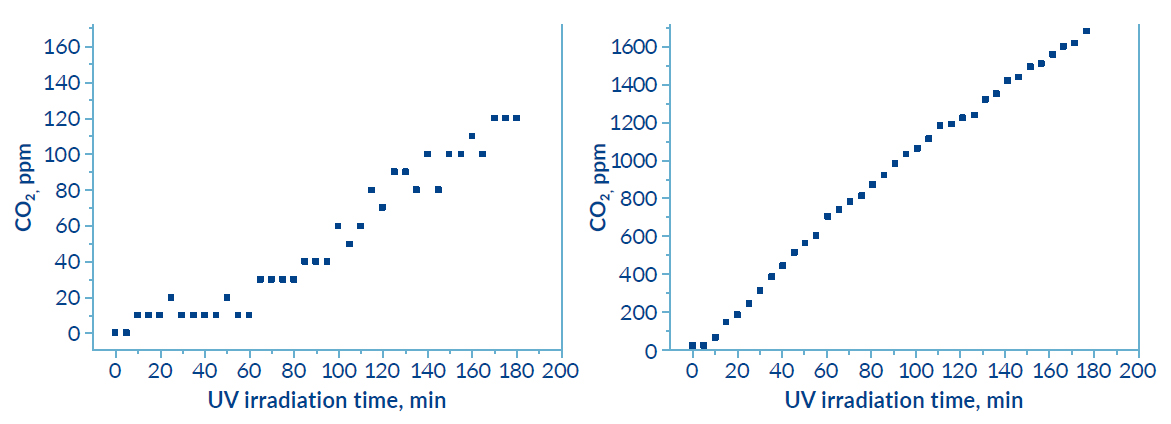
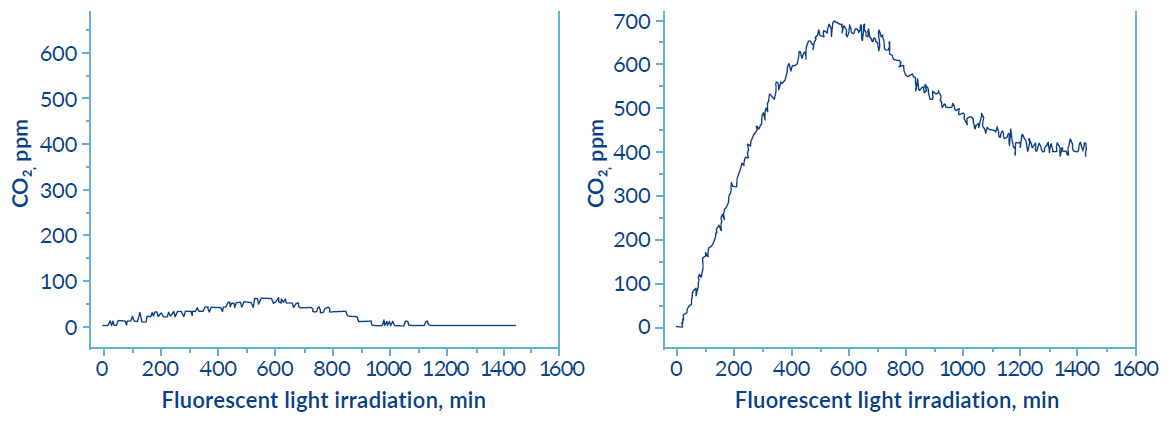
Data generated in collaboration with the University of Lincoln confirmed the conversion of N2O, NO and NO2 to nitrate for plant use. The amount of nitrate produced is directly related to the ppm NOx concentration.
Information supplied by Crop Intellect Ltd.

